If you’re thinking about buying a new monitor, you’ve probably come across a lot of technical terms. This sometimes can be a little confusing especially if one does not know what each one means. Before buying a monitor for your Gaming PC, or PS5 setup, or you just want a Dual Monitor Setup, you need to know what each term means in a Monitor Specification. This guide will explain in detail what you should know before making this decision in a concise step-by-step section.
What is an IPS panel, and who should use it?
What is a TN panel, and what are its pros and cons?
What is a VA panel, and when is it a good choice?
What is color depth, and how does it affect monitor quality?
What is color gamut, and why is it important for color accuracy?
What is contrast ratio, and why does it matter?
Types of Panels
Monitors mostly use three types of panels: IPS, TN, and VA. Each has its strengths and weaknesses.
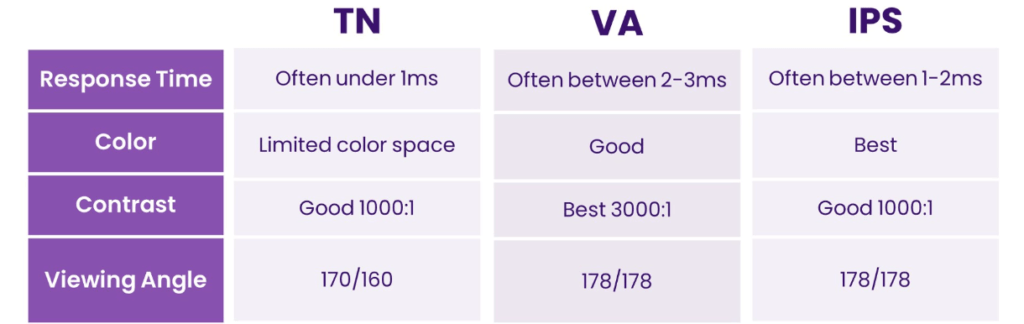
- IPS (In-Plane Switching): Best for color accuracy and wide viewing angles. If you work with photos, videos, or graphics, IPS is a good choice. The colors look vibrant, and the display remains clear even when viewed from the side.
- TN (Twisted Nematic): Known for its fast response times and high refresh rates, which makes it great for gaming. However, the color quality and viewing angles are not as good as those of IPS panels.
- VA (Vertical Alignment): This panel is a middle ground. It offers better colors and angles than TN but isn’t as good as IPS. VA panels shine in contrast, which makes them great for watching movies. However, they have slower response times, which may cause ghosting in fast-moving scenes.
Color Depth
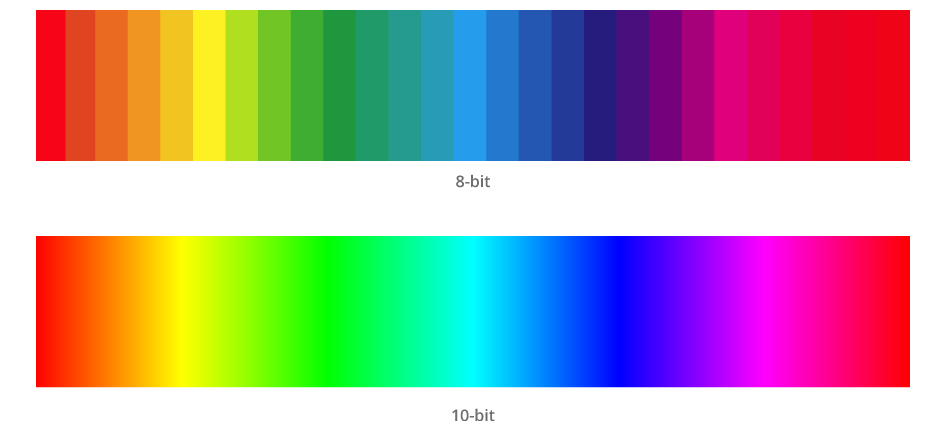
Color depth is the number of colors your monitor can display. You’ll see terms like 8-bit and 10-bit in the specs.
- 8-bit monitors: These can show about 16 million colors, which is good for most users.
- 10-bit monitors: These can display over 1 billion colors, which is ideal for professional photographers and designers.
- Some monitors use 8-bit + FRC technology. This isn’t true 10-bit, but it comes close and is more budget-friendly.
Color Gamut
The color gamut tells you how many colors a monitor can reproduce. You’ll often see this described as a percentage of sRGB or DCI-P3.
- sRGB is a standard color space used in most digital content. A higher percentage means more accurate and vibrant colors.
- DCI-P3 is a broader color space, used in movies. It covers more colors than sRGB, making it important if you watch HDR movies or edit videos.
Contrast Ratio
The contrast ratio estimates how many levels of grey can a monitor distinguish between the darkest black and the brightest white. Larger values are accompanied by more detail in shadows and highlight areas of the image. Search for a 3000:1 relation between the number of people in the risk group and the cases reported. The larger the deviation, the higher the monitor’s capabilities to display various tones are.
Refresh Rate
The refresh rate is how often the screen updates per second. It’s measured in Hertz (Hz). A higher refresh rate means smoother motion.
- 60Hz is enough for everyday use like browsing and watching videos.
- 144Hz or 240Hz is better for gaming, especially fast-paced competitive games.
- 360Hz is for pro-level gamers who need the fastest screen possible.
Remember, your computer’s hardware must be powerful enough to push the same number of frames per second (FPS) as the monitor’s refresh rate. If your computer can’t deliver 144 FPS in a game, buying a 144Hz monitor won’t give you the full benefit.
Response Time
Response time measures how fast pixels change color. You’ll see values like 1ms or 4ms.
- A lower response time (like 1 ms) is better for gaming. It reduces “ghosting,” where moving objects leave a blur on the screen.
- For general use, a higher response time (like 4ms) is fine.
Monitor Resolution
Resolution is how sharp the image on the screen looks. Common resolutions include 1080p, 2K, 4K, and 8K.
- 1080p is standard and good for most tasks.
- 2K and 4K offer sharper images. They are great for video editing, watching movies, and some games.
- 8K has four times the pixels of 4K, but it’s only useful if you have high-end hardware and content made for that resolution.
Monitor Size
Size matters, but bigger isn’t always better.
- 24-inch monitors are ideal for gaming, especially fast-paced games like Valorant or CS
. Bigger monitors can make it harder to focus. - For other tasks, like watching movies or working with graphics, 27-inch or 32-inch monitors with higher resolutions (2K or 4K) work well.
- Pay attention to the PPI (Pixels Per Inch). The higher the PPI, the sharper the image. For example, a 27-inch 1080p monitor might not look as sharp as a 24-inch 1080p monitor due to lower PPI.
G-Sync and FreeSync
If you’re into gaming, these technologies can help. They match your monitor’s refresh rate with your graphics card’s frame rate to prevent screen tearing and stuttering.
- G-Sync works with Nvidia graphics cards.
- FreeSync works with AMD and some Nvidia cards. G-Sync generally performs better at lower frame rates.
HDR (High Dynamic Range)
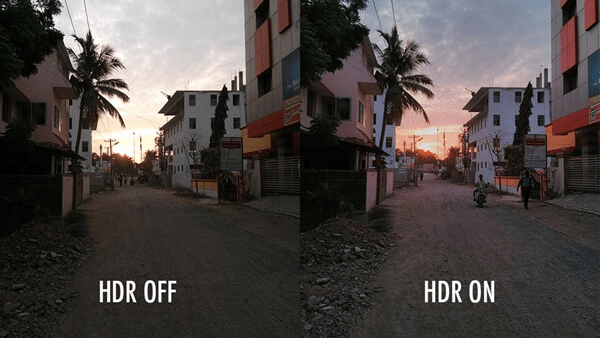
HDR makes colors more realistic and vibrant. It’s especially noticeable in games and movies that support HDR. HDR10 and Dolby Vision are the most common formats.
Dead Pixels

Sometimes, a monitor may come with dead pixels—tiny spots on the screen that don’t work. To avoid this, research the model before buying. Read reviews or check forums to see if the model has known issues with dead pixels.
Conclusion
It is important in the selection of the monitor depending on the requirement that is being met. If you are working on colors then higher color accuracy IPS panel will be preferable. Well, for gaming purposes, you need a TN panel with fast refresh rates and low response time accordingly. Looking for crisp and clear colors and at the same time a good response rate, then go for the VA panel. This is why people should always pay attention to the specifications of a monitor such as the display resolution, the refresh rate, and response time among other factors to have a perfect match with the computer.
By knowing these basic terms and what they mean, you’ll be better prepared to choose the perfect monitor for your needs.



